
什么是elasticsearch?
ElasticSearch是一个分布式,高性能、高可用、可伸缩的搜索和分析系统
什么是Elastic Stack?
Elastic Stack,前身缩写是ELK,就是ElasticSearch + LogStash + Kibana

ES的使用场景:
为什么要使用elasticsearch?
假设用数据库做搜索,当用户在搜索框输入“四川火锅”时,数据库通常只能把这四个字去进行全部匹配。可是在文本中,可能会出现“推荐四川好吃的火锅”,这时候就没有结果了。
ES是一个近实时的搜索引擎(平台),代表着从添加数据到能被搜索到只有很少的延迟。(大约是1s)
Elasticsearch是面向文档的,文档是所有可搜索数据的最小单元。可以把文档理解为关系型数据库中的一条记录。文档会被序列化成json格式,保存在Elasticsearch中。同样json对象由字段组成,给个字段都有自己的类型(字符串,数值,布尔,二进制,日期范围类型)。当我们创建文档时,如果不指定类型,Elasticsearch会帮我们自动匹配类型。每个文档都一个ID,你可以自己指定,也可以让Elasticsearch自动生成。json格式,支持数组/嵌套,在一个index/type里面,你可以存储任意多的文档。注意,尽管一个文档,物理上存在于一个索引之中,文档必须被索引/赋予一个索引的type。
索引是具有某种相似特性的文档集合。例如,您可以拥有客户数据的索引、产品目录的另一个索引以及订单数据的另一个索引。索引由一个名称(必须全部是小写)标识。在单个集群中,您可以定义任意多个索引。Index体现了逻辑空间的概念,每个索引都有自己的mapping定义,用于定义包含文档的字段名和字段类型。Index体现了物理空间的概念,索引中的数据分散在shard上。可以将其暂时理解为 MySql中的 database。
索引的mapping和setting
一个索引可以有多个类型。例如一个索引下可以有文章类型,也可以有用户类型,也可以有评论类型。在一个索引中不能再创建多个类型,在以后的版本中将删除类型的整个概念。
从6.0开始,type已经被逐渐废弃。在7.0之前,一个index可以设置多个types。7.0开始一个索引只能创建一个type(_doc)
节点是一个Elasticsearch实例,本质上就是一个java进程,节点也有一个名称(默认是随机分配的),当然也可以通过配置文件配置,或者在启动的时候,-E node.name=node1指定。此名称对于管理目的很重要,因为您希望确定网络中的哪些服务器对应于ElasticSearch集群中的哪些节点。
在Elasticsearch中,节点的类型主要分为如下几种:
master eligible节点:
每个节点启动后,默认就是master eligible节点,可以通过node.master: false 禁止
master eligible可以参加选主流程,成为master节点
当第一个节点启动后,它会将自己选为master节点
每个节点都保存了集群的状态,只有master节点才能修改集群的状态信息
data节点
可以保存数据的节点。负责保存分片数据,在数据扩展上起到了至关重要的作用
Coordinating 节点
负责接收客户端请求,将请求发送到合适的节点,最终把结果汇集到一起
每个节点默认都起到了Coordinating node的职责
开发环境中一个节点可以承担多个角色,生产环境中,建议设置单一的角色,可以提高性能等
索引可能存储大量数据,这些数据可能会超出单个节点的硬件限制。例如,占用1TB磁盘空间的10亿个文档的单个索引可能不适合单个节点的磁盘,或者速度太慢,无法单独满足单个节点的搜索请求。
为了解决这个问题,ElasticSearch提供了将索引细分为多个片段(称为碎片)的能力。创建索引时,只需定义所需的碎片数量。每个分片(shard)本身就是一个完全功能性和独立的“索引”,可以托管在集群中的任何节点上。
为什么要分片?
如何分配分片以及如何将其文档聚合回搜索请求的机制完全由ElasticSearch管理,并且对作为用户的您是透明的。主分片数在索引创建时指定,后续不允许修改,除非Reindex
在随时可能发生故障的网络/云环境中,非常有用,强烈建议在碎片/节点以某种方式脱机或因任何原因消失时使用故障转移机制。为此,ElasticSearch允许您将索引分片的一个或多个副本复制成所谓的副本分片,简称为副本分片。
为什么要有副本?
总而言之,每个索引可以分割成多个分片。索引也可以零次(意味着没有副本)或多次复制。复制后,每个索引将具有主分片(从中复制的原始分片)和副本分片(主分片的副本)。
可以在创建索引时为每个索引定义分片和副本的数量。创建索引后,您还可以随时动态更改副本的数量。您可以使用收缩和拆分API更改现有索引的分片数量,建议在创建索引时就考虑好分片和副本的数量。
默认情况下,ElasticSearch中的每个索引都分配一个主分片和一个副本,这意味着如果集群中至少有两个节点,则索引将有一个主分片和另一个副本分片(一个完整副本),每个索引总共有两个分片。

1.下载elasticsearch-7.3.2 tar包 下载地址https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/elasticsearch
2.上传到linux,解压 tar -zxvf elasticsearch-7.3.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
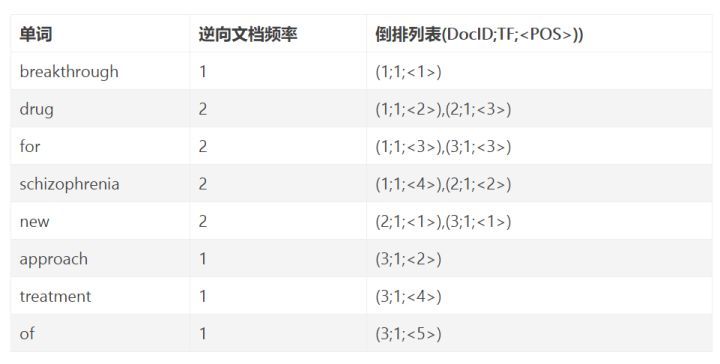
3.进入解压后的 elasticsearch-7.3.2文件夹的bin目录下 执行./elasticsearch
执行结果如下:
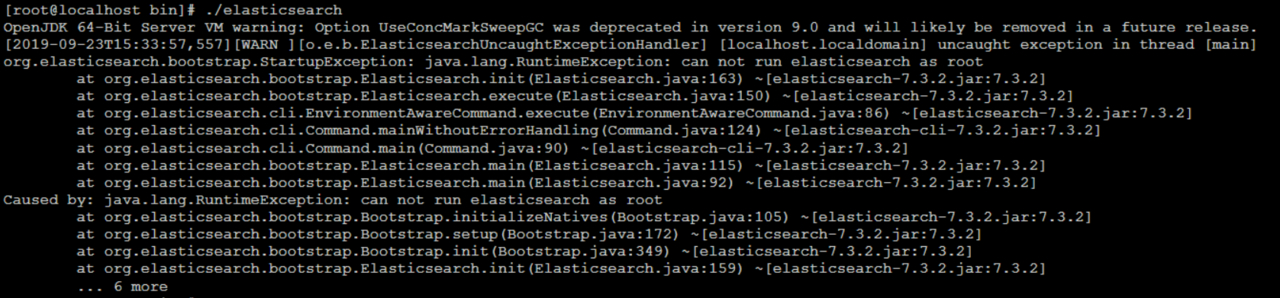
这个错误,是因为使用root用户启动elasticsearch,elasticsearch是不允许使用root用户启动的
在6.xx之前,可以通过root用户启动。但是发现黑客可以透过elasticsearch获取root用户密码,所以为了安全性,在6版本之后就不能通过root启动elasticsearch
解决方案如下:
groupadd taibai
useradd taibai -g taibai
cd /opt [elasticsearch-7.3.2所在路径]
chown -R taibai:taibai elasticsearch-7.3.2
1、调整jvm内存大小(机器内存够也可不调整)
vim config/jvm.options
-Xms512m
-Xmx512m
2、修改network配置,支持通过ip访问
vim config/elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name=luban
node.name=node-1
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
max virtual memory areas vm.max_map_count [65530] is too low, increase to at least [262144]
vm最大虚拟内存,max_map_count[65530]太低,至少增加到[262144]
vim /etc/sysctl.conf
vm.max_map_count=655360
sysctl -p 使配置生效
descriptors [4096] for elasticsearch process likely too low, increase to at least [65536]
最大文件描述符[4096]对于elasticsearch进程可能太低,至少增加到[65536]
vim /etc/security/limits.conf
* soft nofile 65536
* hard nofile 131072
* soft nproc 2048
* hard nproc 4096
* 所有用户
nofile - 打开文件的最大数目
noproc - 进程的最大数目
soft 指的是当前系统生效的设置值
hard 表明系统中所能设定的最大值
max number of threads [2048] for user [tongtech] is too low, increase to at least [4096]
用户的最大线程数[2048]过低,增加到至少[4096]
vim /etc/security/limits.d/90-nproc.conf
* soft nproc 4096
启动:
su taibai
cd /opt/elasticsearch-7.3.2/bin
./elasticsearch 或 ./elasticsearch -d (以后台方式运行)
注意:注意开放端口或者关闭防火墙(centos7)
查询防火墙状态:firewall-cmd --state
关闭防火墙:systemctl stop firewalld.service
开启防火墙: systemctl start firewalld.service
禁止firewall开机启动:systemctl disable firewalld.service
安装成功:
google应用商店下载插件安装(需翻墙):
1.下载kibana-7.3.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/kibana
2.上传至linux系统中并解压 tar -zxvf kibana-7.3.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
3.vim kibana-7.3.2-linux-x86_64/config/kibana.yml
server.port: 5601
server.host: "0.0.0.0"
i18n.locale: "zh-CN"
4.cd kibana-7.3.2-linux-x86_64/bin
5, ./kibana --allow-root
6.访问kibana
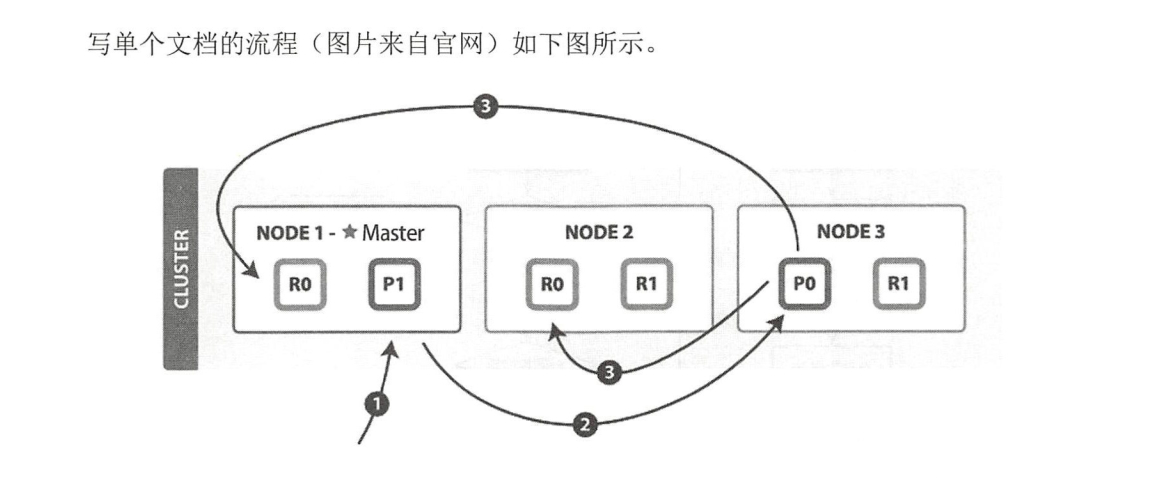
以下是写单个文档所需的步骤:
(1 )客户端向 NODE I 发送写请求。
(2)检查Active的Shard数。
(3) NODEI 使用文档 ID 来确定文档属于分片 0,通过集群状态中的内容路由表信息获知分片 0 的主分片位于 NODE3 ,因此请求被转发到 NODE3 上。
( 4 ) NODE3 上的主分片执行写操作 。 如果写入成功,则它将请求并行转发到 NODE I 和
NODE2 的副分片上,等待返回结果 。当所有的副分片都报告成功, NODE3 将向协调节点报告
成功,协调节点再向客户端报告成功 。
在客户端收到成功响应时 ,意味着写操作已经在主分片和所有副分片都执行完成。
1. 为什么要检查Active的Shard数?
ES中有一个参数,叫做waitforactiveshards,这个参数是Index的一个setting,也可以在请求中带上这个参数。这个参数的含义是,在每次写入前,该shard至少具有的active副本数。假设我们有一个Index,其每个Shard有3个Replica,加上Primary则总共有4个副本。如果配置waitforactiveshards为3,那么允许最多有一个Replica挂掉,如果有两个Replica挂掉,则Active的副本数不足3,此时不允许写入。
这个参数默认是1,即只要Primary在就可以写入,起不到什么作用。如果配置大于1,可以起到一种保护的作用,保证写入的数据具有更高的可靠性。但是这个参数只在写入前检查,并不保证数据一定在至少这些个副本上写入成功,所以并不是严格保证了最少写入了多少个副本。
在以前的版本中,是写一致性机制,现被替换为waitforactiveshards
one:要求我们这个写操作,只要有一个primary shard是active活跃可用的,就可以执行
all:要求我们这个写操作,必须所有的primary shard和replica shard都是活跃的,才可以执行这个写操作
quorum:要求所有的shard中,必须是大部分的shard都是活跃的,可用的,才可以执行这个写操作
写一致性的默认策略是 quorum,即多数的分片(其中分片副本可以是主分片或副分片)在
写入操作时处于可用状态。
put /index/type/id?consistency=quorum
quroum = int( (primary + number_of_replicas) / 2 ) + 1
| 参数 | 简 介 |
|---|---|
| version | 设置文档版本号。主要用于实现乐观锁 |
| version_type | 详见版本类型 |
| op_type | 可设置为 create 。 代表仅在文档不存在时才写入 。 如果文档己存在,则写请求将失败 |
| routing | ES 默认使用文档 ID 进行路由,指定 routing 可使用 routing 值进行路由 |
| wait_for_active_shards | 用于控制写一致性,当指定数量的分片副本可用时才执行写入,否则重试直至超时 。默认为 l , 主分片可用 即执行写入 |
| refresh | 写入完毕后执行 refresh ,使其对搜索可见 |
| timeout | 请求超时时间 , 默认为 l 分钟 |
| pipeline | 指定事先创建好的 pipeline 名称 |
写入Primary完成后,为何要等待所有Replica响应(或连接失败)后返回
在更早的ES版本,Primary和Replica之间是允许异步复制的,即写入Primary成功即可返回。但是这种模式下,如果Primary挂掉,就有丢数据的风险,而且从Replica读数据也很难保证能读到最新的数据。所以后来ES就取消异步模式了,改成Primary等Replica返回后再返回给客户端。
因为Primary要等所有Replica返回才能返回给客户端,那么延迟就会受到最慢的Replica的影响,这确实是目前ES架构的一个弊端。之前曾误认为这里是等waitforactive_shards个副本写入成功即可返回,但是后来读源码发现是等所有Replica返回的。
如果Replica写入失败,ES会执行一些重试逻辑等,但最终并不强求一定要在多少个节点写入成功。在返回的结果中,会包含数据在多少个shard中写入成功了,多少个失败了
PUT /taibai
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": "2", //分片数
"number_of_replicas": "0", //副本数
"write.wait_for_active_shards": 1
}
}
修改副本数
PUT taibai/_settings
{
"number_of_replicas" : "2"
}
DELETE /taibai
//指定id
POST /taibai/_doc/1001
{
"id":1001,
"name":"张三",
"age":20,
"sex":"男"
}
//不指定id es帮我们自动生成
POST /taibai/_doc
{
"id":1002,
"name":"三哥",
"age":20,
"sex":"男"
}
在Elasticsearch中,文档数据是不为修改的,但是可以通过覆盖的方式进行更新
PUT /taibai/_doc/1001
{
"id":1009,
"name":"太白",
"age":21,
"sex":"哈哈"
}
其实es内部对partial update的实际执行和传统的全量替换方式是几乎一样的,其步骤如下
POST /taibai/_update/1001
{
"doc":{
"age":23
}
}
替换和更新的不同:替换是每次都会去替换,更新是有新的东西就更新,没有新的修改就不更新,更新比替换的性能好
DELETE /taibai/_doc/1001
GET /taibai/_doc/6_h43W0BdTjVHQ-cgnv2
GET /taibai/_search 默认最多返回10条数据
POST /bank/_search
{
"query": { "match_all": {} },
"sort": [
{
"属性名": {
"order": "asc"
}
}
]
}
took Elasticsearch运行查询需要多长时间(以毫秒为单位)
timed_out 搜索请求是否超时
_shards 搜索了多少碎片,并对多少碎片成功、失败或跳过进行了细分。
max_score 找到最相关的文档的得分
hits.total.value 找到了多少匹配的文档
hits.sort 文档的排序位置(当不根据相关性得分排序时)
hits._score 文档的相关性评分(在使用match_all时不适用)
GET /taibai/_search?q=age:23 查询年龄等于23的
POST /taibai/_search
{
"query" : {
"match" : { //查询年龄等于23的
"age" : 23
}
}
}
//查询地址等于mill或者lane
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": { "match": { "address": "mill lane" } }
}
//查询地址等于(mill lane)的
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": { "match_phrase": { "address": "mill lane" } }
}
//注意:match 中如果加空格,那么会被认为两个单词,包含任意一个单词将被查询到
//match_parase 将忽略空格,将该字符认为一个整体,会在索引中匹配包含这个整体的文档。
POST /taibai/_search //查询年龄大于20 并且性别是男的
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gt": 20
}
}
},
"must": {
"match": {
"sex": "男"
}
}
}
}
}
POST /taibai/_search //这里会分词搜索
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "张三"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"name": {}
}
}
}
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.x/search-aggregations.html
例如:查询平均年龄 (如果不指定size等于0,则还会返回10条数据)
POST /bank/_search
{
"aggs": {
"taibai": { //自定义名字
"avg": { //什么类型
"field": "age" //那个字段
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
使用脚本
POST /bank/_search
{
"aggs": {
"taibai": {
"avg": {
"script": {
"source": "doc.age.value"
}
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
例如:
POST /bank/_search
{
"aggs": {
"taibai": {
"cardinality": {
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
POST /bank/_search
{
"aggs": {
"taibai": {
"extended_stats": {
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
可以理解为统计个数
基于某个field,该 field 内的每一个【唯一词元】为一个桶,并计算每个桶内文档个数。默认返回顺序是按照文档个数多少排序。
POST /bank/_search
{
"aggs": {
"taibai": {
"terms": {
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
获取到每组前n条数据,相当于sql 中Top(group by 后取出前n条)。它跟踪聚合中相关性最高的文档
POST /bank/_search
{
"aggs": {
"taibai": {
"terms": {
"field": "age"
},
"aggs": {
"count": {
"top_hits": {
"size": 3
}
}
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
POST bank/_search
{
"aggs": {
"group_by_age": {
"range": {
"field": "age",
"ranges": [
{
"from": 20,
"to": 30
},
{
"from": 30,
"to": 40
},
{
"from": 40,
"to": 50
}
]
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
如果使用浏览器工具去查询,返回的json没有格式化,可在后面加参数pretty,返回格式化后的数据
http://192.168.204.209:9200/taibai/_doc/_fiK3W0BdTjVHQ-c0HvY?pretty
GET /taibai/_doc/9_iK3W0BdTjVHQ-czHuE?_source=id,name //只返回id和name字段
GET /taibai/_source/9_iK3W0BdTjVHQ-czHuE
还可以去掉元数据并且返回指定字段
GET /taibai/_source/9_iK3W0BdTjVHQ-czHuE?_source=id,name
HEAD /taibai/_doc/9_iK3W0BdTjVHQ-czHuE
语法实例
POST _bulk
{ "index" : { "_index" : "test", "_id" : "1" } }
{ "field1" : "value1" }
{ "delete" : { "_index" : "test", "_id" : "2" } }
{ "create" : { "_index" : "test", "_id" : "3" } }
{ "field1" : "value3" }
{ "update" : {"_id" : "1", "_index" : "test"} }
{ "doc" : {"field2" : "value2"} }
如果,某一条数据不存在,不影响整体响应,需要通过found的值进行判断是否查询到数据。
POST /taibai/_mget
{
"ids" : [ "8fiK3W0BdTjVHQ-cxntK", "9fiK3W0BdTjVHQ-cy3sI" ]
}
POST _bulk
{ "create" : { "_index" : "taibai", "_id" : "3" } }
{"id":2002,"name":"name1","age": 20,"sex": "男"}
{ "create" : { "_index" : "taibai", "_id" : "4" } }
{"id":2003,"name":"name1","age": 20,"sex": "男"}
POST _bulk
{ "delete" : { "_index" : "taibai", "_id" : "8PiK3W0BdTjVHQ-cxHs1" } }
{ "delete" : { "_index" : "taibai", "_id" : "6vh43W0BdTjVHQ-cHXv8" } }
POST _bulk
{ "update" : {"_id" : "4", "_index" : "taibai"} }
{ "doc" : {"name" : "太白"} }
{ "update" : {"_id" : "3", "_index" : "taibai"} }
{ "doc" : {"name" : "太白"} }
GET /taibai/_search?size=1&from=2 size: 结果数,默认10 from: 跳过开始的结果数,默认0
前面我们创建的索引以及插入数据,都是由Elasticsearch进行自动判断类型,有些时候我们是需要进行明确字段类型的,否则,自动判断的类型和实际需求是不相符的。
自动判断的规则如下:
| JSON type | Field type |
|---|---|
| Boolean: true or false | "boolean" |
| Whole number: 123 | "long" |
| Floating point: 123.45 | "double" |
| String, valid date: "2014-09-15" | "date" |
| String: "foo bar" | "string" |
创建明确类型的索引:
PUT /goods
{
"settings": {
"number_of_replicas": 0,
"number_of_shards": 1
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "long"
},
"sn": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"name": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"price": {
"type": "double"
},
"num": {
"type": "integer"
},
"alert_num": {
"type": "integer"
},
"image": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"images": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"weight": {
"type": "double"
},
"create_time": {
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
},
"update_time": {
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
},
"spu_id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"category_id": {
"type": "integer"
},
"category_name": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_smart"
},
"brand_name": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"spec": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"sale_num": {
"type": "integer"
},
"comment_num": {
"type": "integer"
},
"status": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
添加一个字段到现有的映射
PUT /luban/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"isold": { //字段名
"type": "keyword", //类型
"index": false
}
}
}
更新字段的映射
除了支持的映射参数外,您不能更改现有字段的映射或字段类型。更改现有字段可能会使已经建立索引的数据无效。
如果您需要更改字段映射,创建具有正确映射一个新的索引和重新索引的数据转换成指数。
重命名字段会使在旧字段名称下已建立索引的数据无效。而是添加一个alias字段以创建备用字段名称。
查看索引的映射
GET /luban/_mapping
查看指定字段的映射信息
GET /luban/_mapping/field/name
term 主要用于精确匹配哪些值,比如数字,日期,布尔值或 not_analyzed 的字符串(未经分析的文本数据类型):
POST /taibai/_search
{
"query" : {
"term" : {
"age" : 20
}
}
}
terms 跟 term 有点类似,但 terms 允许指定多个匹配条件。 如果某个字段指定了多个值,那么文档需要一起去
做匹配:
POST /taibai/_search
{
"query" : {
"terms" : {
"age" : [20,27]
}
}
}
range 过滤允许我们按照指定范围查找一批数据:
gt :: 大于
gte :: 大于等于
lt :: 小于
lte :: 小于等于
POST /taibai/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 20,
"lte": 22
}
}
}
}
exists 查询可以用于查找文档中是否包含指定字段或没有某个字段,类似于SQL语句中的 IS_NULL 条件
包含这个字段就返回返回这条数据
POST /taibai/_search
{
"query": {
"exists": {
"field": "name"
}
}
}
match 查询是一个标准查询,不管你需要全文本查询还是精确查询基本上都要用到它。
如果你使用 match 查询一个全文本字段,它会在真正查询之前用分析器先分析 match 一下查询字符;如果用 match 下指定了一个确切值,在遇到数字,日期,布尔值或者 not_analyzed 的字符串时,它将为你搜索你
给定的值:
POST /taibai/_search
{
"query" : {
"match" : {
"name" : "三个小矮人"
}
}
}
match查询会先对搜索词进行分词,分词完毕后再逐个对分词结果进行匹配,因此相比于term的精确搜索,match是分词匹配搜索
bool 查询可以用来合并多个条件查询结果的布尔逻辑,它包含一下操作符:
must :: 多个查询条件的完全匹配,相当于 and 。
must_not :: 多个查询条件的相反匹配,相当于 not 。
should :: 至少有一个查询条件匹配, 相当于 or 。
这些参数可以分别继承一个查询条件或者一个查询条件的数组:
POST /taibai/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"term": {
"sex": "男"
}
},
"must_not": {
"term": {
"age": "29"
}
},
"should": [
{
"term": {
"sex": "男"
}
},
{
"term": {
"id": 1003
}
}
]
}
}
}
查询年龄为20岁的用户。
POST /taibai/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"term": {
"age": 20
}
}
}
}
}
该数据是使用www.json- http://generator.com/生成的,因此请忽略数据的实际值和语义,因为它们都是随机生成的。您可以从这里下载示例数据集(accounts.json)。将其提取到当前目录,然后按如下方式将其加载到集群中:
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XPOST "localhost:9200/bank/_bulk?pretty&refresh" --data-binary "@accounts.json"
官方文档练习案例:
1.给指定id加点年龄(age)
2.执行match_all操作,并按帐户余额降序对结果进行排序,并返回前10个
3.如何从搜索中返回两个字段,即帐号和余额
4.返回帐户为20的
5.回地址中包含“mill”的所有帐户
6.返回地址中包含“mill”或“lane”的所有帐户
7.返回地址中包含“mill”和“lane”的所有帐户
8.地址中既不包含“mill”也不包含“lane”的所有帐户
9.返回所有40岁但不居住在ID的人(state不等于ID)的账户
10.使用bool查询返回余额在20000到30000之间的所有帐户,包括余额。换句话说,我们希望找到余额大于或等于20000,小于或等于30000的账户
11.按状态(state)对所有帐户进行分组,然后返回按count降序排列的前10个
12.按状态计算平均帐户余额(同样只针对按count降序排列的前10个状态)
13.基于之前(12)的聚合,我们现在按降序对平均余额排序
14.按照年龄等级(20-29岁,30-39岁,40-49岁)分组,然后按性别分组,最后得到每个年龄等级,每个性别的平均账户余额
| Standard | 默认分词器 按词分类 小写处理 |
|---|---|
| Simple | 按照非字母切分,非字母则会被去除 小写处理 |
| **Stop ** | 小写处理 停用词过滤(the,a, is) |
| **Whitespace ** | 按空格切分 |
| **Keyword ** | 不分词,当成一整个 term 输出 |
| **Patter ** | 通过正则表达式进行分词 默认是 \W+(非字母进行分隔) |
| **Language ** | 提供了 30 多种常见语言的分词器 |
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer":"standard",
"text":"tai bai"
}
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer":"standard",
"text":"决战到天亮"
}
英文分词 一般以空格分隔,中文分词的难点在于,在汉语中没有明显的词汇分界点,如果分隔不正确就会造成歧义。
常用中文分词器,IK、jieba、THULAC等,推荐使用IK分词器。
IK分词器 Elasticsearch插件地址:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik
注意选择对应es的版本

1.下载项目 zip包
2.解压项目
3.进入项目跟目录 使用maven编译打包此项目
mvn clean
mvn compile
mvn package
4.执行完上面命令后 在{project_path}/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/target/releases/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-*.zip会有个zip,上传到linux elasticsearch 插件目录, 如: plugins/ik 注意在plugins下新建ik目录 将zip包上传到ik目录下
**
**
5.使用unzip命令解压zip包,没有unzip的 可先下载unzip 命令:yum install -y unzip zip
6.解压之后删除原来的zip包
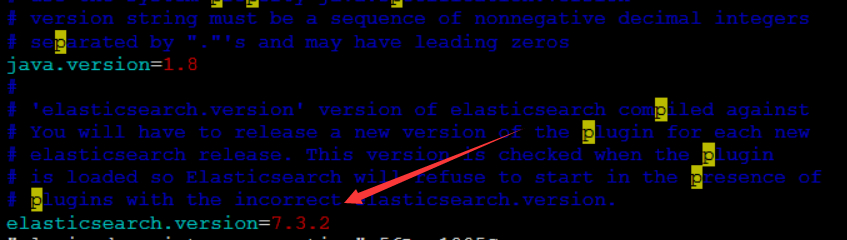
7.检查是否需要修改版本信息
vim {path}/plugins/ik/plugin-descriptor.properties
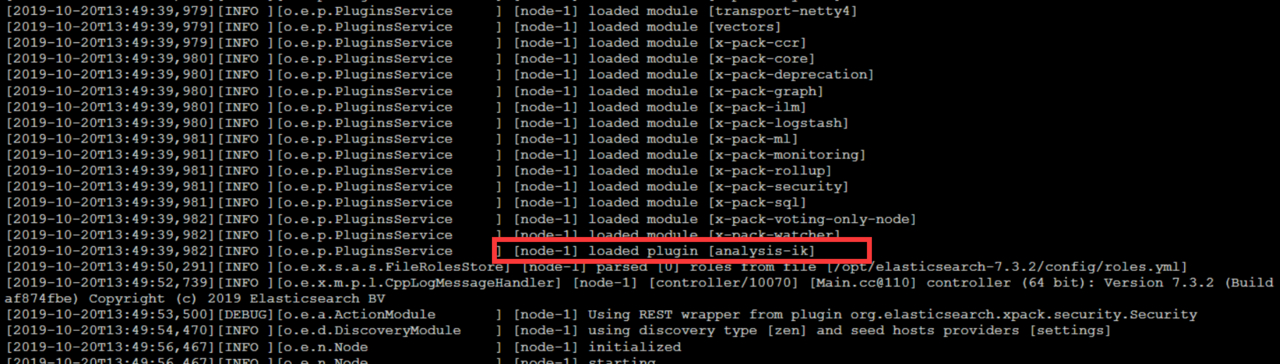
8.重启 ik插件安装完成
9.测试中文分词器效果
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word", 或者 //ik_smart
"text": "决战到天亮"
}
1.下载对应版本的zip包https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-pinyin/releases
2.可在Windows解压好,在plugins下创建pinyin文件夹
3.将解压内容放置在pinyin文件夹,重启
接受参数
| tokenizer | 一个内置的或定制的tokenizer。(必需) |
|---|---|
| char_filter | 一个可选的内置或自定义字符过滤器数组。 |
| filter | 一个可选的内置或定制token过滤器数组。 |
PUT my_index
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"my_custom_analyzer": {
"type": "custom",
"tokenizer": "standard",
"char_filter": [
"html_strip" //过滤HTML标签
],
"filter": [
"lowercase", //转小写
"asciifolding" //ASCII-折叠令牌过滤器 例如 à to a
]
}
}
}
}
}
POST my_index/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "my_custom_analyzer",
"text": "Is this <b>déjà vu</b>?"
}
创建一个中文+拼音的分词器(中文分词后拼音分词)
PUT my_index
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"ik_pinyin_analyzer": {
"type": "custom",
"tokenizer": "ik_smart",
"filter": [
"pinyin_max_word_filter"
]
},
"ik_pingying_smark": {
"type": "custom",
"tokenizer": "ik_smart",
"filter": [
"pinyin_smark_word_filter"
]
}
},
"filter": {
"pinyin_max_word_filter": {
"type": "pinyin",
"keep_full_pinyin": "true", #分词全拼如雪花 分词xue,hua
"keep_separate_first_letter": "true",#分词简写如雪花 分词xh
"keep_joined_full_pinyin": true #分词会quanpin 连接 比如雪花分词 xuehua
},
"pinyin_smark_word_filter": {
"type": "pinyin",
"keep_separate_first_letter": "false", #不分词简写如雪花 分词不分词xh
"keep_first_letter": "false" #不分词单个首字母 如雪花 不分词 x,h
}
}
}
}
}
PUT /my_index/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"productName": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_pinyin_analyzer", #做文档所用的分词器
"search_analyzer":"ik_pingying_smark" #搜索使用的分词器
}
}
}
POST /my_index/_doc
{
"productName": "雪花啤酒100L"
}
GET /my_index/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"productName": "雪Hua"
}
}
}
PUT /test
{
"settings": {
"index": {
"number_of_shards": "1",
"number_of_replicas": "0"
}
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"email": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"hobby": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
POST _bulk
{ "create" : { "_index" : "test","_id": "1000"} }
{"name":"张三","age": 20,"mail": "111@qq.com","hobby":"羽毛球、乒乓球、足球"}
{ "create" : { "_index" : "test","_id": "1001"} }
{"name":"李四","age": 21,"mail": "222@qq.com","hobby":"羽毛球、乒乓球、足球、篮球"}
{ "create" : { "_index" : "test","_id": "1002"} }
{"name":"王五","age": 22,"mail": "333@qq.com","hobby":"羽毛球、篮球、游泳、听音乐"}
{ "create" : { "_index" : "test","_id": "1003"} }
{"name":"赵六","age": 23,"mail": "444@qq.com","hobby":"跑步、游泳、篮球"}
{ "create" : { "_index" : "test","_id": "1004"} }
{"name":"孙七","age": 24,"mail": "555@qq.com","hobby":"听音乐、看电影、羽毛球"}
POST /test/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"hobby": "音乐"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"hobby": {}
}
}
}
//搜索包含音乐和篮球的
POST /test/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"hobby": "音乐 篮球"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"hobby": {}
}
}
}
//搜索包含音乐还有篮球的(and)
POST /test/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"hobby": {
"query": "音乐 篮球",
"operator": "and"
}
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"hobby": {}
}
}
}
GET /goods/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 1000,
"lte": 2000
}
}
},
{
"match": {
"name": "2018女鞋"
}
},
{
"match": {
"spec": "红色 黑色"
}
}
],
"must_not": [
{
"match": {
"spec": "蓝色"
}
}
]
}
}
}
//在Elasticsearch中也支持这样的查询,通过minimum_should_match来指定匹配度,如:70%;
POST /test/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"hobby": {
"query": "游泳 羽毛球",
"minimum_should_match": "70%"
}
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"hobby": {}
}
}
}
//搜索结果中必须包含篮球,不能包含音乐,如果包含了游泳,那么它的相似度更高。
POST /test/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"match": {
"hobby": "篮球"
}
},
"must_not": {
"match": {
"hobby": "音乐"
}
},
"should": [{
"match": {
"hobby": "游泳"
}
}]
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"hobby": {}
}
}
}
//默认情况下,should中的内容不是必须匹配的,如果查询语句中没有must,那么就会至少匹配其中一个。当然了,
也可以通过minimum_should_match参数进行控制,该值可以是数字也可以的百分比。
//minimum_should_match为2,意思是should中的三个词,至少要满足2个
POST /test/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [{
"match": {
"hobby": "游泳"
}
},
{
"match": {
"hobby": "篮球"
}
},
{
"match": {
"hobby": "音乐"
}
}
],
"minimum_should_match": 2
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"hobby": {}
}
}
}
搜索关键字为“游泳篮球”,如果结果中包含了“音乐”权重为10,包含了“跑步”权重为2。
POST /test/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"match": {
"hobby": {
"query": "游泳篮球",
"operator": "and"
}
}
},
"should": [{
"match": {
"hobby": {
"query": "音乐",
"boost": 10
}
}
},
{
"match": {
"hobby": {
"query": "跑步",
"boost": 2
}
}
}
]
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"hobby": {}
}
}
}
cluster.name: luban
node.name: node-1
node.master: true
node.data: true
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
#参数设置一系列符合主节点条件的节点的主机名或 IP 地址来引导启动集群。
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
# 设置新节点被启动时能够发现的主节点列表(主要用于不同网段机器连接)
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.204.209","192.168.204.203","192.168.204.108"]
# 该参数就是为了防止”脑裂”的产生。定义的是为了形成一个集群,有主节点资格并互相连接的节点的最小数目。
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2
# 解决跨域问题配置
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
cluster.name: luban
node.name: node-3
node.master: true
node.data: true
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.204.209","192.168.204.203","192.168.204.108"]
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
cluster.name: luban
node.name: node-2
node.master: true
node.data: true
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.204.209","192.168.204.203","192.168.204.108"]
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
启动后效果
注意修改jvm.options
cluster.name: luban
node.name: node-1
node.master: true
node.data: true
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
transport.port: 9300
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.204.209:9300", "192.168.204.209:9301","192.168.204.209:9302"]
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
cluster.name: luban
node.name: node-2
node.master: true
node.data: true
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9201
transport.port: 9301
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.204.209:9300", "192.168.204.209:9301","192.168.204.209:9302"]
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
cluster.name: luban
node.name: node-3
node.master: true
node.data: true
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9202
transport.port: 9302
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.204.209:9300", "192.168.204.209:9301","192.168.204.209:9302"]
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
分别启动:
./elasticsearch -p /tmp/elasticsearch_9200_pid -d
./elasticsearch -p /tmp/elasticsearch_9201_pid -d
./elasticsearch -p /tmp/elasticsearch_9202_pid -d
新建目录:
注意赋予权限
chown -R taibai:taibai ES
分别启动:
./elasticsearch -d -E node.name=node-1 -E http.port=9200 -E transport.port=9300 -E path.data=/ES/data/node1 -E path.logs=/ES/logs/node1
./elasticsearch -d -E node.name=node-2 -E http.port=9201 -E transport.port=9301 -E path.data=/ES/data/node2 -E path.logs=/ES/logs/node2
./elasticsearch -d -E node.name=node-3 -E http.port=9202 -E transport.port=9302 -E path.data=/ES/data/node3 -E path.logs=/ES/logs/node3
https://blog.csdn.net/jiankunking/article/details/65448030
https://blog.csdn.net/lixiaohai_918/article/details/89569611
查看插件命令:./elasticsearch-plugin list
下载插件命令:./elasticsearch-plugin install analysis-icu